A power supply unit (PSU) converts mains AC to low-voltage regulated DC power for the internal components of a computer. Modern personal computers universally use a switched-mode power supply. Some power supplies have a manual selector for input voltage, while others automatically adapt to the supply voltage. Most modern desktop personal computer power supplies conform to the ATX specification, which includes form factor and voltage tolerances.

The desktop computer power supply changes alternating current from a wall socket to low-voltage direct current to operate the processor and peripheral devices. Several direct-current voltages are required and they must be regulated with some accuracy to provide stable operation of the computer. A power supply rail or voltage rail refers to a single voltage provided by a power supply unit (PSU). Although the term is generally used in electronic engineering, many people, especially computer enthusiasts, encounter it in the context of personal computer power supplies.
Computer power supplies may have short circuit protection, overpower (overload) protection, overvoltage protection, undervoltage protection, overcurrent protection, and over temperature protection. Recent power supplies have a standby voltage available, to allow most of the computer system to be powered off. When the computer is powered down but the power supply is still on, it can be started remotely via Wake-on-LAN and Wake-on-ring or locally via Keyboard Power ON (KBPO) if the motherboard supports it.
Connectors
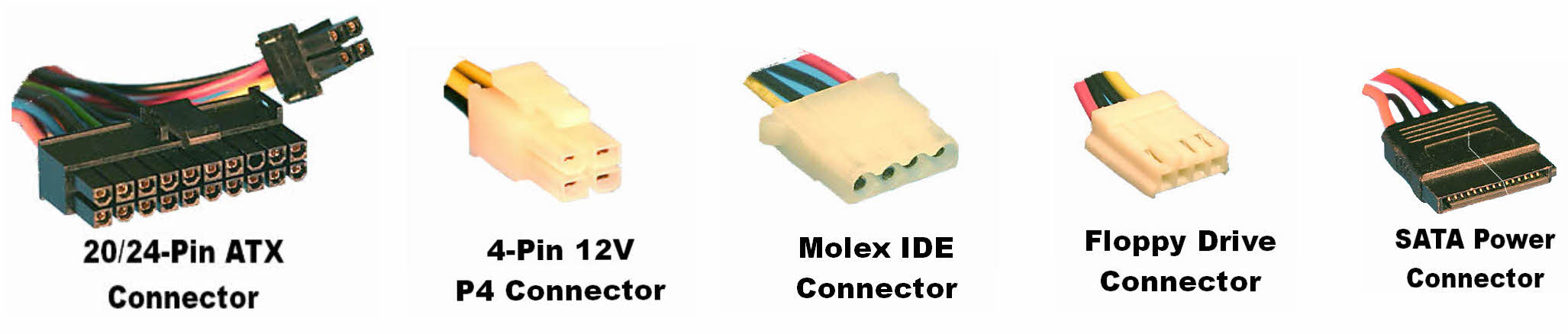
Various connectors from a computer PSU.
Typically, power supplies have the following connectors (all are Molex (USA) Inc Mini-Fit Jr, unless otherwise indicated):
- PC Main power connector (usually called P1): This is the connector that goes to the motherboard to provide it with power. The connector has 20 or 24 pins. One of the pins belongs to the PS-ON wire (it is usually green). This connector is the largest of all the connectors. In older AT power supplies, this connector was split in two: P8 and P9. A power supply with a 24-pin connector can be used on a motherboard with a 20-pin connector. In cases where the motherboard has a 24-pin connector, some power supplies come with two connectors (one with 20-pin and other with 4-pin) which can be used together to form the 24-pin connector.
- 12V only power connector (labelled P1, though it is not compatible with the ATX 20 or 24 pin connector): This is a 16-pin Molex connector supplying the motherboard with six 12V lines with common returns, a 'supply OK' signal, a 'PSU ON' signal and an 11V auxiliary supply. One pin is left unused.
- 12V only System monitoring (P10): This is a 171822-8 AMP or equivalent connector carrying a supply to the PSU fan and sense returns.
- ATX12V 4-pin power connector (also called the P4 power connector). A second connector that goes to the motherboard (in addition to the main 24-pin connector) to supply dedicated power for the processor. For high-end motherboards and processors, more power is required, therefore EPS12V has an 8-pin connector.
- 4-pin Peripheral power connectors: These are the other, smaller connectors that go to the various disk drives of the computer. Most of them have four wires: two black, one red, and one yellow. Unlike the standard mains electrical wire color-coding, each black wire is a ground, the red wire is +5 V, and the yellow wire is +12 V. In some cases these are also used to provide additional power to PCI cards such as FireWire 800 cards.
- 4-pin Molex (Japan) Ltd power connectors (usually called Mini-connector or "mini-Molex"): This is one of the smallest connectors that supplies a 3 1/2 inch floppy drive with power. In some cases, it can be used as an auxiliary connector for AGP video cards. Its cable configuration is similar to the Peripheral connector.
- Auxiliary power connectors: There are several types of auxiliary connectors designed to provide additional power if it is needed.
- Serial ATA power connectors: a 15-pin connector for components which use SATA power plugs. This connector supplies power at three different voltages: +3.3, +5, and +12 volts.
- 6-pin Most modern computer power supplies include 6-pin connectors which are generally used for PCI Express graphics cards, but a newly introduced 8-pin connector should be seen on the latest model power supplies. Each PCI Express 6-pin connector can output a maximum of 75 W.
- 6+2 pin For the purpose of backwards compatibility, some connectors designed for use with high end PCI Express graphics cards feature this kind of pin configuration. It allows either a 6-pin card or an 8-pin card to be connected by using two separate connection modules wired into the same sheath: one with 6 pins and another with 2 pins.
- A IEC 60320 C14 connector with an appropriate C13 cord is used to attach the power supply to the local power grid.
Modular power supplies
A modular power supply provides a detachable cable system, offering the ability to remove unused connections at the expense of a small amount of extra electrical resistance introduced by the additional connector. This reduces clutter, removes the risk of dangling cables interfering with other components, and can improve case airflow. Many modular supplies have some permanent multi-wire cables with connectors at the ends, such as PC main and 4-pin Molex, though newer supplies marketed as "Fully Modular" allow even these to be disconnected.
Life span
Life span is usually measured in mean time between failures (MTBF). Higher MTBF ratings are preferable for longer device life and reliability. Quality construction consisting of industrial grade electrical components or a larger or higher speed fan can help to contribute to a higher MTBF rating by keeping critical components cool. Overheating is a major cause of PSU failure. Calculated MTBF value of 100,000 hours (about 11 years continuous operation) is not uncommon.